Introduction: Why Your Smart Lock Needs a Bodyguard
Imagine this — you’re heading out for a weekend getaway. You lock your front door with a quick tap on your phone, hop into the car, and feel that little sigh of relief because technology’s got your back. But what if, while you’re sipping coffee miles away, someone else figures out a way to “digitally” jiggle that lock open?
Smart locks are like superheroes in the world of home security — fast, convenient, and pretty darn smart. But just like any superhero, they have their weaknesses. Hackers can try to exploit these weaknesses if you’re not careful. The good news? With the right habits and tools, you can make your smart lock so secure that even the sneakiest cyber-thief will walk away shaking their head.
Let’s walk through how hackers target smart locks, the risks involved, and — most importantly — how to prevent smart lock hacking at home without needing a degree in computer science.
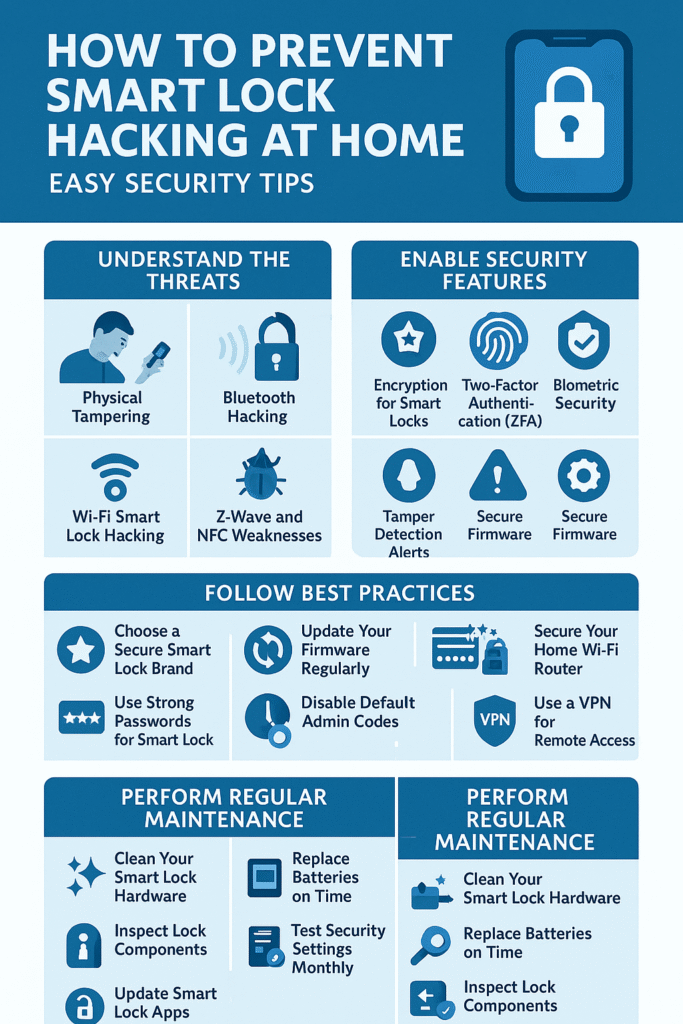
Chapter 1: Understanding the Enemy — How Hackers Target Smart Locks
1. Physical Tampering
This is the old-school approach. A thief tries to force the lock open with tools, bump keys, or even by damaging the casing.
It’s rare with strong locks, but still possible if your smart lock has weak hardware.
2. Bluetooth Hacking
Some smart locks use Bluetooth to connect to your phone. Hackers can use “signal sniffing” to intercept and replicate Bluetooth signals — kind of like recording your key press and replaying it.
3. Wi-Fi Smart Lock Hacking
Wi-Fi makes remote access convenient, but if your network is insecure, hackers can break in digitally — just like guessing the password to your social media account.
4. Z-Wave and NFC Weaknesses
These are other wireless protocols used by certain smart locks. If they’re not encrypted well, hackers can “listen” to the communication between your lock and your hub.
Chapter 2: Smart Lock Security Features That Keep Hackers Out
Encryption for Smart Locks
Think of encryption as your lock’s secret language. Even if someone hears the conversation, they can’t understand it without the “decoder ring.”
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
This is like having two locks on your door — one digital and one password-based. Even if a hacker gets one, they still can’t get in.
Biometric Security
Fingerprints and facial recognition add another layer of protection that’s hard to copy.
Tamper Detection Alerts
Some smart locks send you a notification if someone is physically messing with them.
Secure Firmware
Firmware is the lock’s internal “brain.” Regular updates patch security holes hackers might try to exploit.
Chapter 3: Best Practices to Prevent Smart Lock Hacking
1. Choose a Secure Smart Lock Brand
Not all locks are created equal. Go for brands that have a solid reputation for security, good customer support, and regular firmware updates.
2. Update Your Firmware Regularly
Skipping updates is like leaving your door unlocked. Companies release updates to fix weaknesses hackers might exploit.
3. Use Strong Passwords for Smart Lock Apps
Avoid “123456” or “password.” Mix uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols. Example: M@pLe2025!
4. Limit Guest Access Codes
Give guests a temporary code that expires after their stay — especially if you rent out your place on Airbnb.
5. Disable Default Admin Codes
Many smart locks ship with a factory-set master code. Change it immediately.
6. Monitor Access Logs
Most smart locks track who opened the door and when. Review these logs for anything suspicious.
7. Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Remote Access
Public Wi-Fi is like shouting your password in a crowded street. Use mobile data or a VPN instead.
8. Secure Your Home Wi-Fi Router
Set a strong Wi-Fi password, turn on WPA3 encryption, and change the router’s default admin credentials.
9. Use a VPN for Remote Access
A VPN adds an extra layer of encryption to your connection.
Chapter 4: Maintenance Habits That Boost Security
- Clean Your Smart Lock Hardware to prevent dust from jamming sensors.
- Replace Batteries on Time to avoid lockouts or emergency bypass modes.
- Inspect Lock Components for cracks or tampering signs.
- Test Security Settings Monthly to ensure everything still works.
- Update Smart Lock Apps so you’re running the latest security features.
Chapter 5: Advanced Protection Methods
Deadbolt Reinforcement
Use a reinforced strike plate and longer screws to make forced entry harder.
Security Cameras with Smart Locks
Cameras create a visual record and scare off intruders.
Integration with Alarm Systems
If the lock is breached, your alarm can sound instantly.
Door Sensors
They alert you if the door opens unexpectedly.
Activity Notifications
Instant alerts for every unlock or lock event.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting Smart Lock Security Issues
- Connectivity Problems – Check Wi-Fi or Bluetooth range, restart the lock, or update firmware.
- App Glitches – Clear the app cache or reinstall it.
- Compromised Lock – Reset it to factory settings and change all codes.
- Report Hacking Attempts – Contact your lock’s manufacturer and, if needed, local authorities.
Chapter 7: Special Tips for Different Environments
- Apartment Security – Use locks that don’t require drilling, so you can keep your landlord happy while staying secure.
- Airbnb Safety – Change guest codes after every checkout and monitor access logs.
- Vacation Homes – Pair your lock with security cameras and remote monitoring.
- Offices – Use role-based access codes for employees.

Conclusion: Making Hackers Give Up Before They Even Try
Smart locks can be as safe — or safer — than traditional locks, but only if you treat them like the high-tech devices they are. That means regular maintenance, strong passwords, firmware updates, and smart usage habits.
Think of your smart lock as the goalie in your home’s security game. You can’t just hope it blocks every shot — you have to give it the best defense possible. Follow these steps, and hackers will be moving on to easier targets.
